
How To Rank Your Law Firm’s Website 1st in Google, Guaranteed
What’s the best way to market a law firm in 2022? Depends who you ask.
Some lawyers are sticking to traditional methods, while others are going digital.
Online paid ads are growing in popularity among attorneys, but is it the best route for growing leads (and clients)?
Not quite.
In my 15 years of helping law firms drive leads and conversions, there’s only one method that trumps all.
Organic search.
There’s nothing like ranking on page one of Google. And I know this because I’ve helped hundreds of law firms gain free traffic and leads.
How’d I do it? We’ll discuss that today. Continue reading to see how SEO can boost your law firm’s visibility and growth.
Check out our videos for deeper insights, or tune in to our Podcast for legal marketing insights on the go.
Why SEO vs other marketing channels?
First, let’s analyze why other marketing tactics a waste of time (and money) for law firms.
Google PPC is costly
In case you’re new, paid search works like this…
Someone types in a query for a local law firm, and search results appear with ads at the top.
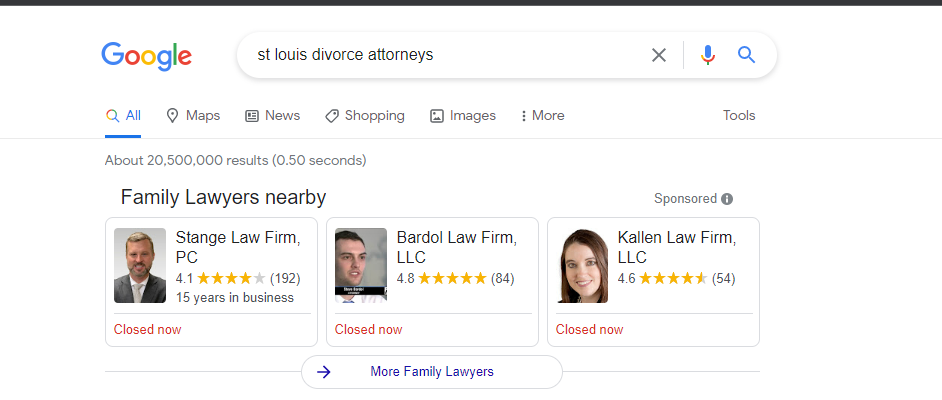
But is it worth it?
If you know what you’re doing…yes.
If you’re spending tens of thousands on ads and struggling to generate and/or close the leads, then most definitely not.
DO PPC RIGHT: Complete guide to Pay Per Click Ad campaigns for law firms
Social media ads do not convert well
Facebook. Tiktok. Instagram. LinkedIn. All the popular social media platforms have ad programs available. Seems like a no-brainer strategy to get your law firm in front of a ton of people.
But there’s a caveat: social media users are there to socialize and scroll through their feeds to find interesting conversations. Not download an eBook or contact a service provider.
Plus, ads are annoying and often overlooked, making them less effective than search ads. In fact, a Ruler Analytics survey shows paid social only drives a 6% conversion rate for phone leads in the legal sector.
Not impressive.
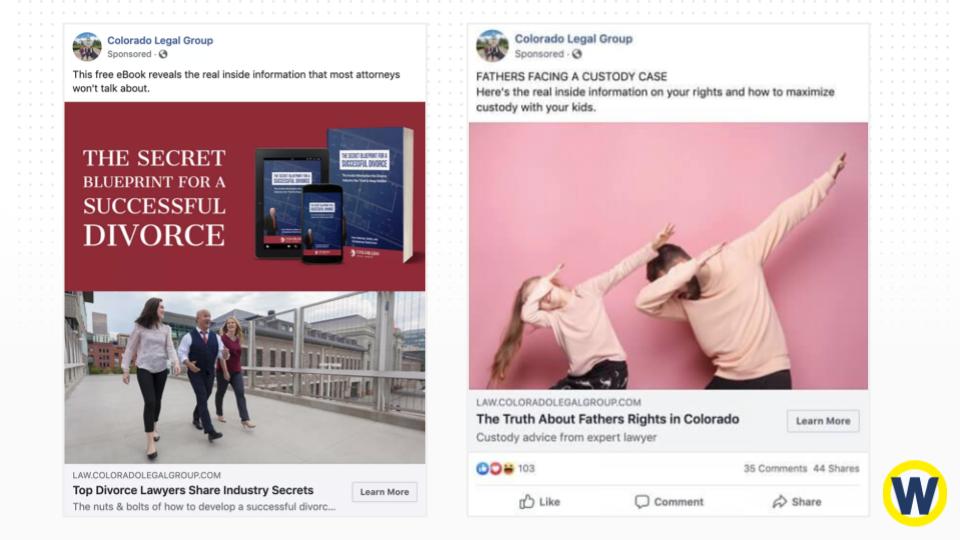
But it makes sense—the need for an attorney isn’t something you stumble upon. You don’t see an ad on Facebook and think, “Gee, I do need a DUI lawyer right now.”
When a person needs a lawyer, they head to Google and search for one. And this is an excellent example of the power of search engine optimization. Once you understand how to use it to your benefit, you’ll find it’s simple, cost-effective, and profitable.
Organic social is too much work
Unfortunately, not all organic marketing is created equal. While SEO works phenomenally on Google, you don’t see the same impact on social media.
Publishing content, engaging with others, and offering your expertise are excellent for brand building. But it’s not the proper tool for growing leads and customers.
For one, it takes up a ton of time and energy (which you’re already limited by). And two, it doesn’t guarantee you’ll reach a particular audience who’s currently looking for legal assistance.
So here’s what to do instead.
No one sees your ads on bus benches, radio and billboards
Traditional ads, such as those found on buses, benches, billboards, and even radios, are prominent in the legal industry. I consistently see bus benches plastered with attorney ads in Miami.
But the reality is, most people aren’t going to pay attention, let alone write down your phone number to call you. Heck, most people drive a vehicle and don’t have the time or desire to.

Now, this isn’t to say they don’t have a place, because they do. For example, large law firms with hundreds of locations and thousands of attorneys make reaching the masses a valid goal.
At this level, your top priority is brand awareness, which makes reach essential. However, this approach won’t drive immediate customers to your doorstep.
It’s a long and expensive branding strategy. And honestly, they don’t work all that well for revenue growth.
If your primary focus is acquisition, then your best bet isn’t on out-of-home ads.
Dive deeper: THIS Is The BEST Way To Generate Leads For Law Firms In 2024
SEO traffic is plentiful and converts the highest
Organic traffic is a gem that keeps on giving. It grows in perpetuity, unlike ads that require you to spend money to make money. Paid ad results are like a staircase—the more you want to earn, the more you must invest.
The cost of acquisition continues to climb, making it harder to grow your ROI.
SEO, on the other hand, continuously grows, thanks to the many keywords you can target. Eventually, you’ll gain the infamous hockey stick growth.
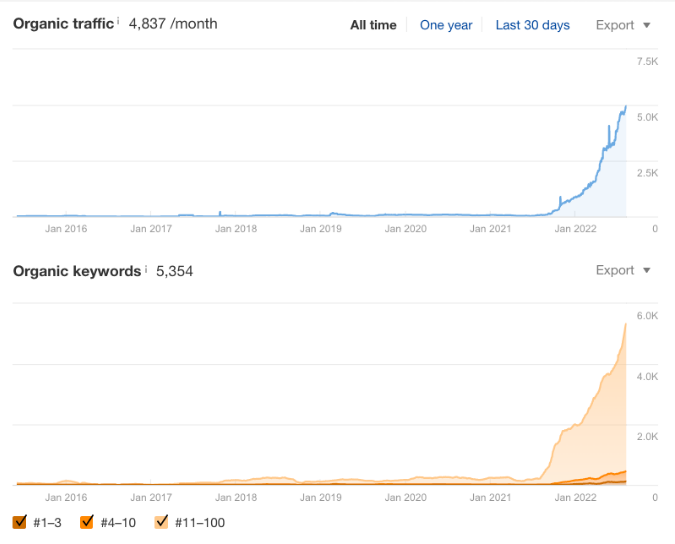
It’s also worth noting that nearly 66% of calls in the legal sector stem from organic search. We can attest to this.
Brotman Law worked with us last year to grow its organic sessions by 200% and client call bookings by 178% using purely SEO.
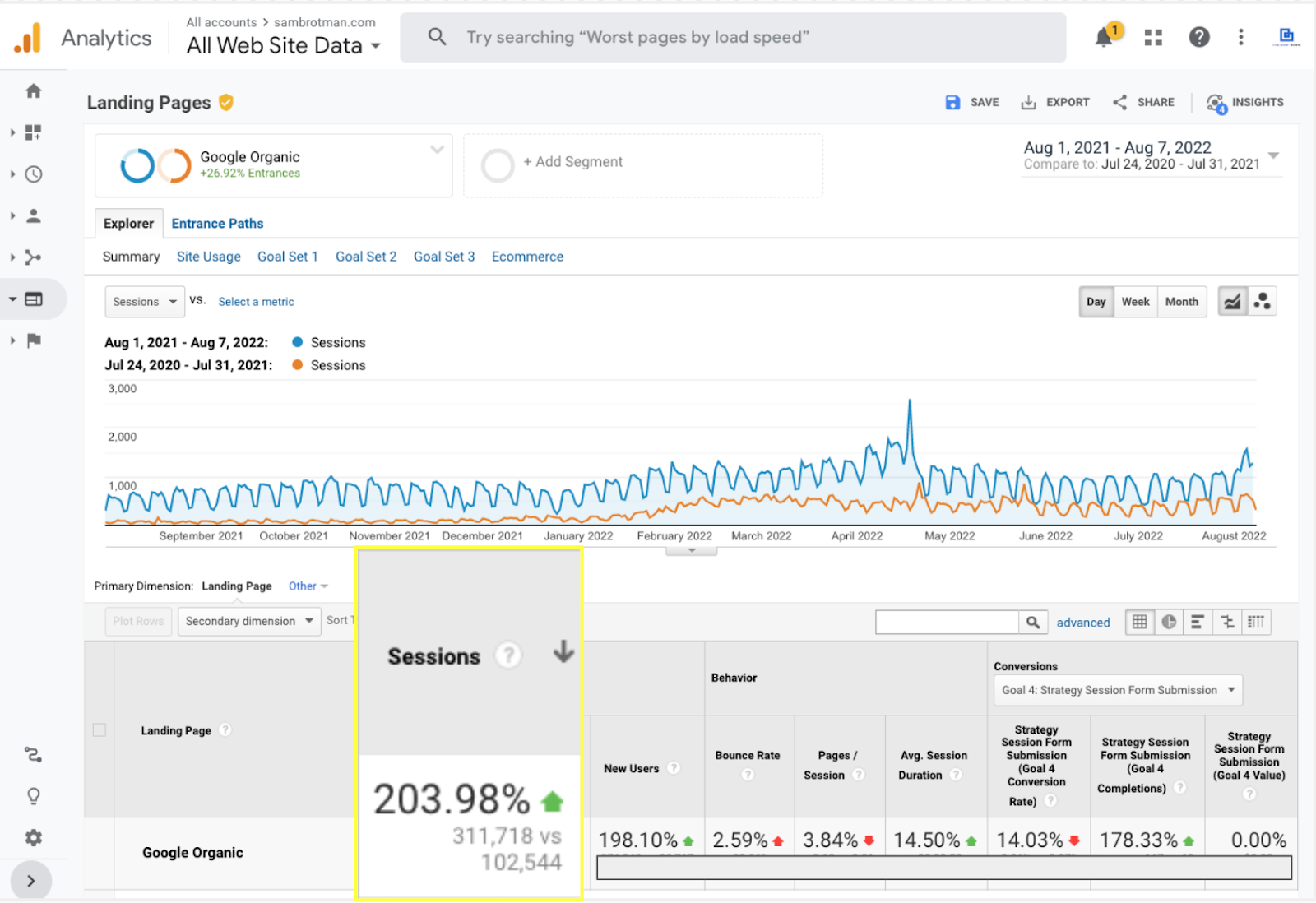
Not bad, considering it’s all from free traffic.
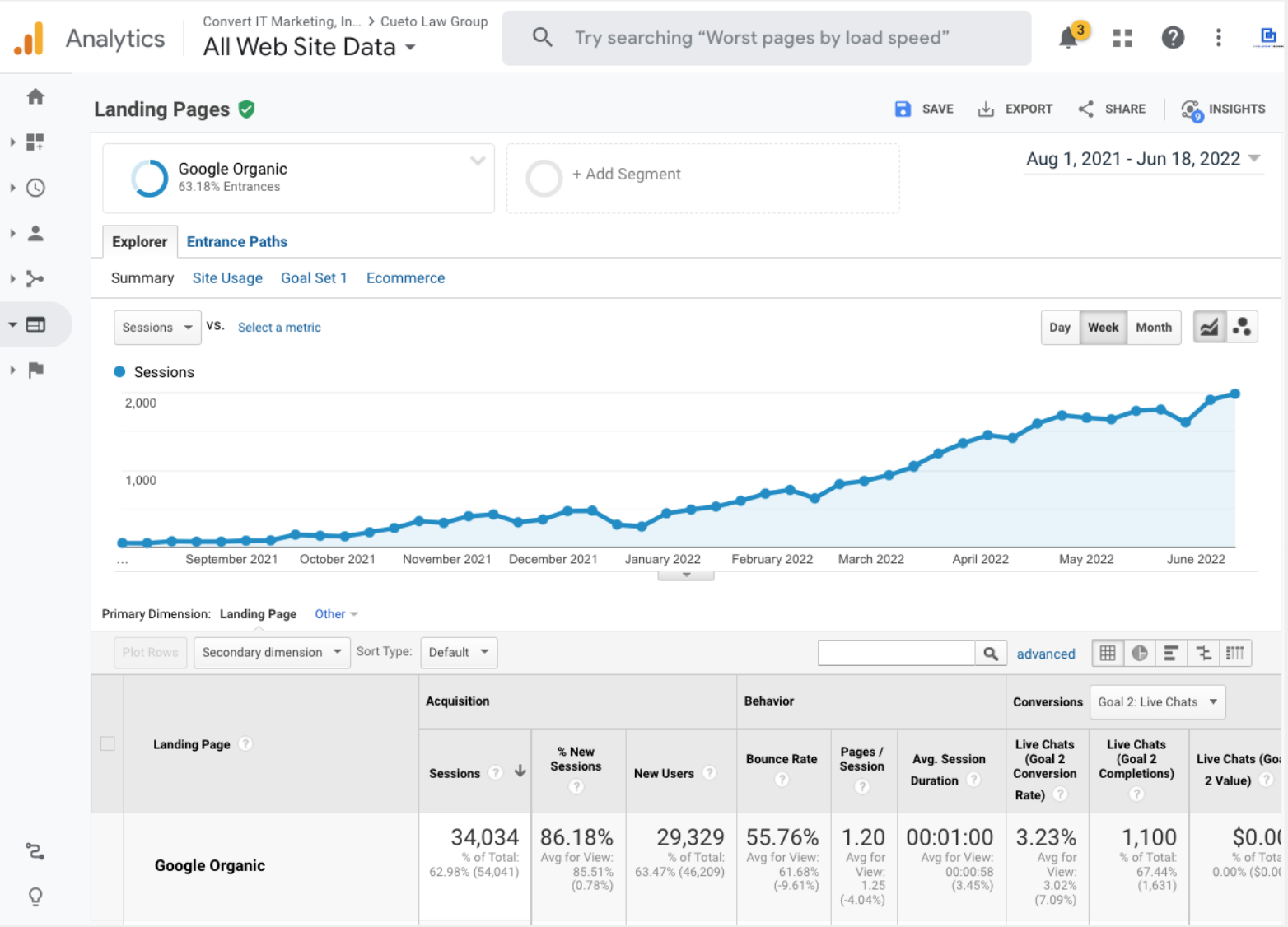
And this isn’t a one-time thing—we see the same with all of our clients. For example, we’re currently working with Cueto Law Group, which we helped grow traffic for using free traffic:
Our simple 4-part SEO strategy for law firms
At WEBRIS, we’re all about simplicity. We live and work by this concept using the Pareto Principle:
Focus your time and energy on doing things that’ll move the needle, and do it exceptionally well.
It requires using 20% input to drive 80% of your output. This philosophy couldn’t be truer for SEO strategies.
Here’s what to focus on for maximum output.
1. Optimize your local Google Business profile
Your target customers are in your locale and use Google to find your legal services. So it makes sense to optimize your Google Business Profile. Doing so will boost your visibility in local search results.
Local search is when a search term includes a city, county, state, or other geographical terms to localize the results.
For example, when you type in “DUI attorney Miami,” it triggers the Maps Pack:
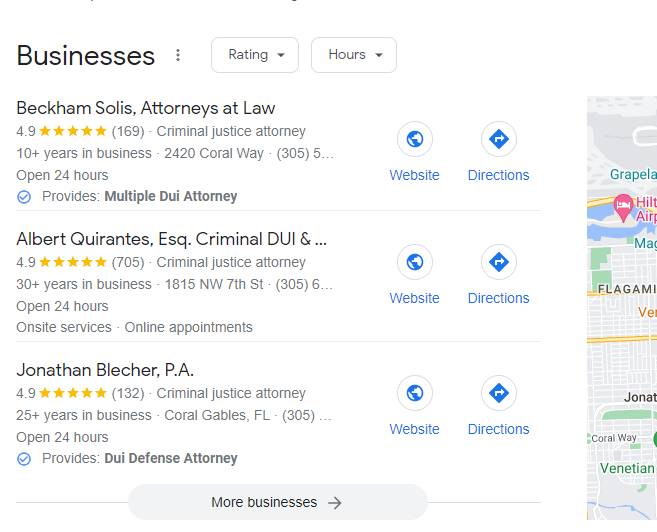
It showcases a list of DUI attorneys in Miami next to a map. This should be a target because it includes your website link, business hours, phone number, and directions—perfect for guiding prospects straight to your office.
To rank in the top three, you need a verified physical location and a business profile optimized for local search specifically.
Here’s how to optimize your profile:
- Verify your physical address (Google will mail you a postcard with a code)
- Solicit clients for positive reviews across the web using email outreach (Google, Avvo, FindLaw etc.)
- Tag relevant categories
- Keep your listing active with updated images, numbers, addresses, business hours, live chats
- Claim or create business citations in local business directories (Yelp, Bing Places, Yellow Pages, etc.)
Google will use these indicators to determine your ranking position in local search and the Map Pack.
2. Clean up your website’s structure
The wrong website structure makes it hard for Google search engine bots to crawl, index, and rank your pages. So get this right early to prevent hurting your website’s position in search engine results pages (SERPs).
How do you optimize your site structure? It’s more on the technical side, but isn’t difficult. It’s about having the right pages on your site:
- Home page
- Practice areas
- About Us
- Contact
- Results/Testimonials/Case studies
- Blog
Other nice-to-haves are:
- FAQ
- Scholarships/Sponsorships
- Spanish version of all pages
You’ll find this similar structure on popular legal websites, such as Morgan & Morgan. Here’s the home page:
Along the top, you find the site structure. It includes everything we listed above and more.
Here’s their results page, which is critical to have for obvious reasons:
And here’s Rubenstein Law’s practice areas page:
Don’t overlook including additional pages, like an FAQ page to address concerns prospects may have that could block them from contacting your firm:
Categorize the questions based on practice areas or themes if you only have a single-practice firm. Not only does this help visitors find answers faster (without bothering your office)—it’s also helpful for SEO.
Aside from capturing keywords for higher rankings, scholarship pages can help with getting backlinks from blogs, educational directories, and press websites.

The more sites linking to yours show Google your content is relevant and worth ranking high. Plus, it’s a natural process—no need to reach out to sites to link back to your scholarship page.
Then based on where you’re located, it’s ideal to have a link to your site in a different language such as Spanish (or another prominent language in your target area). This is useful for folks who don’t speak English as a first language, and it’ll give you some SEO juice on Spanish Google.
Hire a freelance translator or use a translation tool, then use an editor to clean it up.
3. Create content that informs and educates
Here’s where you build the roads to drive traffic to your website. Content is what ranks best and what people search for on Google.
So you’ll need to develop informative blog posts to educate your audience and potentially guide them to a conversion. The idea is to help visitors understand legal processes and how your firm may help them with their situation.
Note that many of your site’s visitors will include folks who aren’t ready for your services. These are people who are playing the field, looking for answers before determining they need legal representation.
Ideally, you want to publish at least one blog post weekly. For example, my agency builds 20 pages, schedules them to publish weekly, and then promotes them to legal audiences.
Consistently publishing content shows Google your site is fresh and relevant. And you may even get backlinks from other sites that find your content valuable.
Now, you have these folks in your ecosystem, but remember—this isn’t direct marketing traffic. When someone sees a blog post, they don’t instantly become a customer. So the goal is spreading your footprint and growing that exponential hockey curve.
This is where informational content comes in.
Question is, “What type of content should attorneys write?”
There are three types of content lawyers should create to build a funnel that guides visitors through the customer journey:
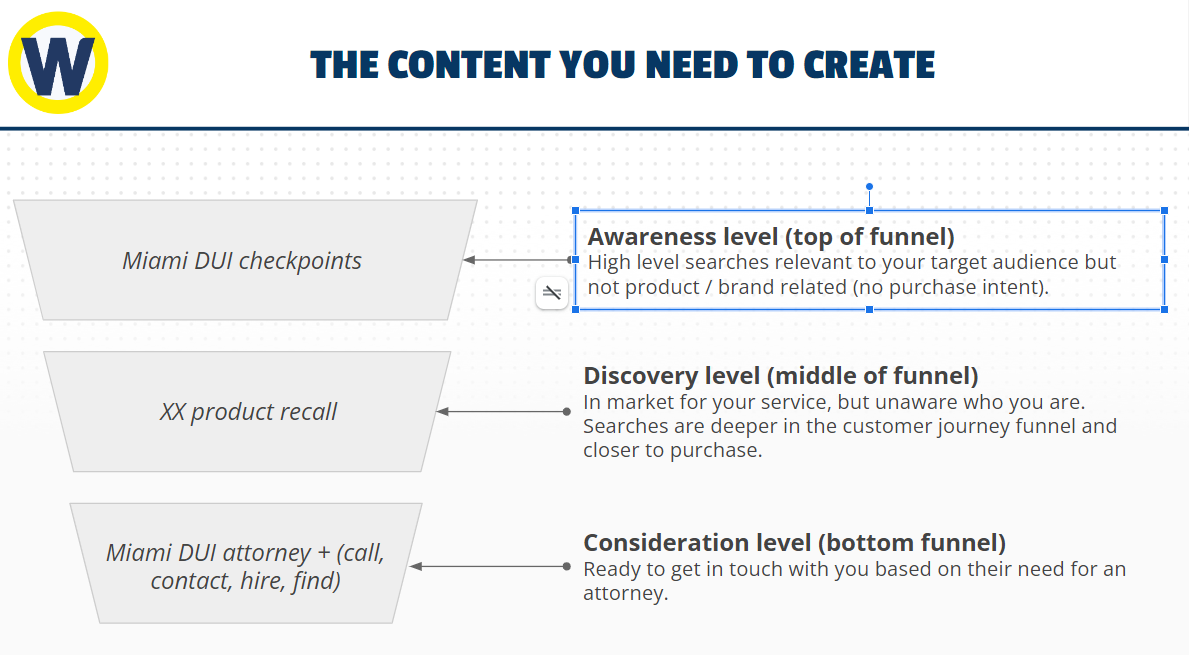
Everyone that visits your site won’t be at the same stage. By crafting content for each, you can guide each person closer to the end goal: a conversion.
Top of the funnel content
Top of the funnel visitors aren’t aware they have a legal issue. So these are the least likely to convert at the get-go. They conduct high-level searches unrelated to your law firm or service. So they’re not looking for an attorney at this point.
Yet, they may look up DUI checkpoints in Miami. Why? Because they likely had a DUI in the past and want to prevent getting another when they go out partying tonight. It’s unfortunate, but this puts these individuals in the market for your services in the future.

By creating content around this topic, you put your law firm on their radar for when they land in jail for a DUI.
Middle of the funnel content
People in the middle of the funnel are aware of their problem and are looking for a solution. So the intent of their search is deeper and closer to a purchase. For instance, if they look up a product recall, odds are they purchased the item and saw the recall on the news.

Now, they’re on Google looking for an attorney’s help. At this stage, they’re looking to discover solutions to their problem. And since there are a lot more people in the middle who are a step away from a conversion, you want to focus 80% of your content here.
This isn’t just about scaling traffic (like at the top of the funnel)—it’s about scaling phone calls to your office.
Bottom of the funnel content
When a person understands there’s a problem and the solutions available, they’re ready to pay for help. They’re one step from a conversion, giving you plenty of opportunity to attract their attention and consideration.
This is when people zone in on content in the middle funnel, which should drive them to relevant bottom of the funnel pages, like:
- Service pages
- Results pages
- Contact page
These will contain keywords like “Miami DUI attorney,” “call Miami DUI attorney,” or “hire DUI attorney Miami.”
Your content at the awareness and discover stage should guide traffic through the funnel to scale your growth exponentially.
Here’s an example of how a DUI attorney’s funnel may look:
- Awareness: “New DUI Law and How it Affects Arizona Drivers” with a link at the end to a middle of the funnel post
- Discovery: “5 Things to Avoid When You Get Arrested for DUI” with a link at the end to a case study page
- Consideration: “How Our Law Firm Helped Hundreds Walk Free After a DUI” with a link at the end to the contact page
It’s all about your call to action (CTA) at the end, which leads blog visitors to other relevant pages on the site that move them through the funnel.
In this example, Morgan and Morgan has a personal injury service page with a call to action to fill out their form for a free consultation:
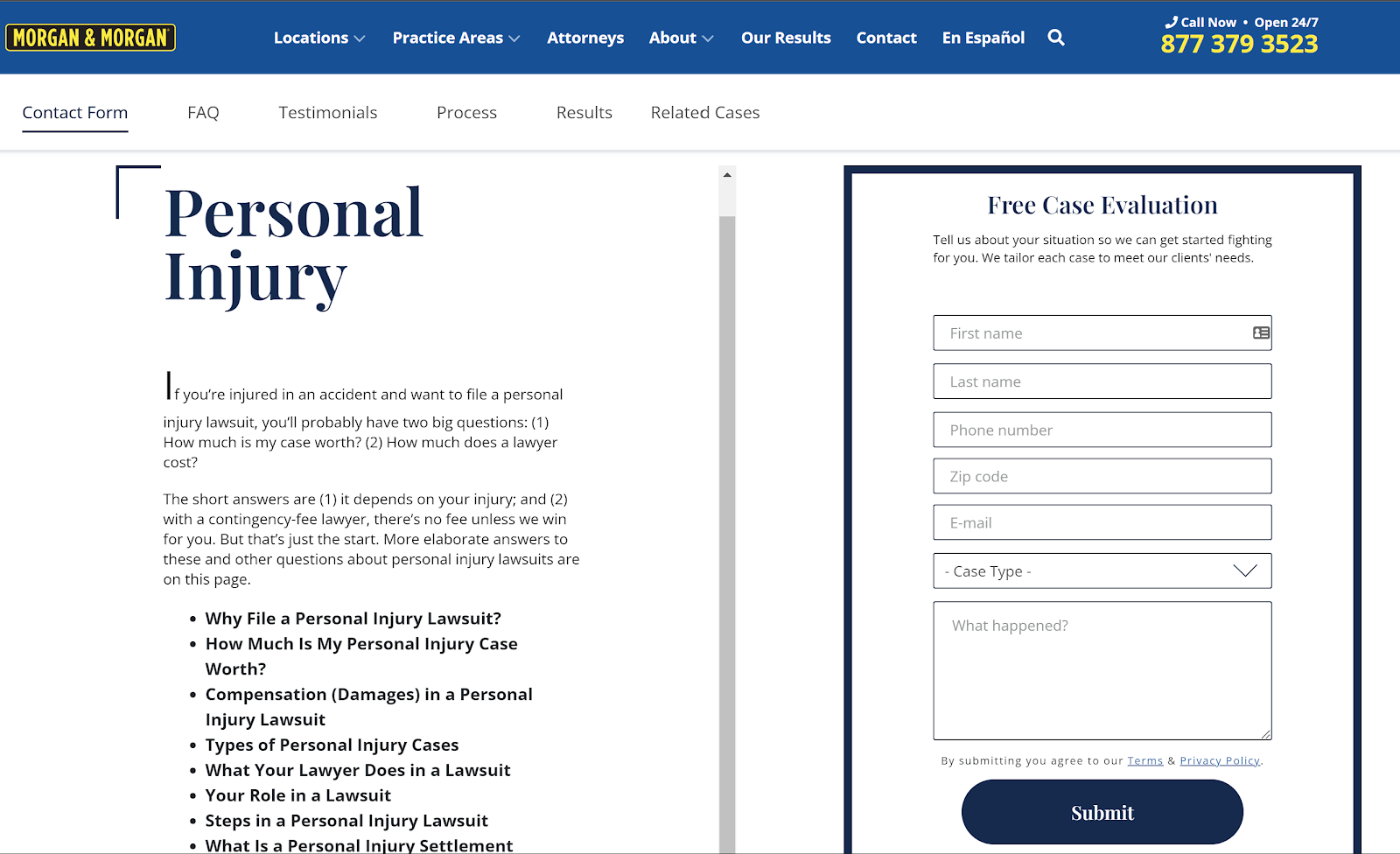
4. Building backlinks to your pages
Website structure helps Google crawl your pages and content targets keywords to help your site rank. Now, it’s time to build your site’s authority in the eyes of Google and your visitors. Because with authority comes trust, which increases your ranking and conversion potential.
When a blog post is mentioned on a credible legal blog or press site, it tells Google your site is trustworthy. It’s like being vouched for by a known celebrity. Plus, it drives traffic from these sources, further proving your relevancy.
Creating high-value content filled with expert insights and actionable tips makes it easier to get backlinks from notables, like news sites and law magazines. The more links (aka votes) you get, the more it helps your ranking.
But not all links are created equal.
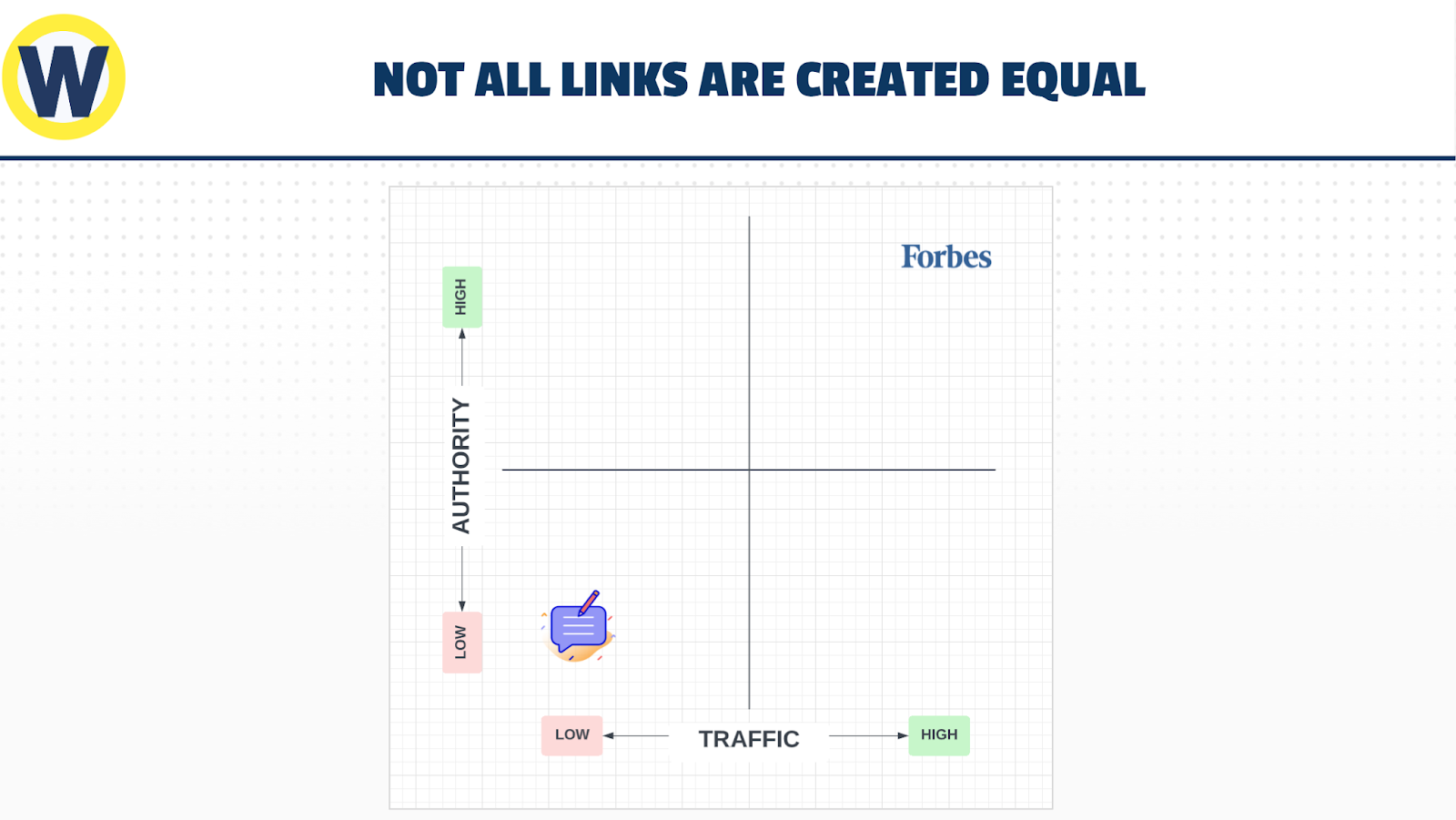
In the chart, sites in the lower left quadrant are from low authority and low traffic (not a suitable backlink). Then in the upper right quadrant, you have Forbes with high traffic and authority (the best link possible).
So a backlink from Forbes gives you a higher vote of authority than getting one in a low traffic, low authority site. In fact, Google may not count this backlink at all. So your focus should be on gathering links from sites with high traffic and/or high authority—and that’s relevant to your industry and audience.
It’s more powerful to get a backlink from a legal journal than a technology website.
Now, there are three types of backlink building attorneys should focus on:
- PR links: Public relations agencies work to get you articles on news sites (e.g., Forbes, Bloomberg, etc.)
- HARO links: Help a Reporter Out is a resource to find articles to contribute quotes to in exchange for a backlink to your website
- Legal websites/blogs: Non-competitive websites in the legal niche that link to your articles, include your quote, or that publish your guest post
| Link Type | Pros | Cons |
| PR Links |
|
|
| HARO Links |
|
|
| Legal Blogs |
|
|
We use a combination of all three to help law firms scale backlinking rapidly. I even have a database of legal sites we worked with before that I reach out to for writing and quote opportunities.
The outcome is increased traffic and conversions for our clients.
SEO is awesome, but requires a lot of work—we can help
You’re an attorney with an endless to-do list. While SEO is proven to help law firms scale, it requires a lot of time and effort you can’t afford to spend.
This is why we recommend partnering with an attorney SEO agency that understands your industry and audience. It ensures you get all the benefits of implementing in-depth SEO strategies.
We’ll analyze your data from Google Analytics, top competitors, and the total addressable market. Then we run growth models to see the expected return for your investment in our firm.
When you hire us, you know what to anticipate in return for your investment.
Interested in learning more? Contact our growth team to learn how we can scale your law firm.
Your Website Is Losing Money!
Find out how many leads your website SHOULD be getting through our Traffic Projection Analysis.
FIND OUT MOREIs Your Website Costing You Clients?
Is Your Website Costing You Clients?
Find out how many new cases your website SHOULD be getting through our Traffic Projection Analysis.
A data driven analysis that accurately forecasts how much traffic (and cases) your website should be getting from Google each month.
BOOK MY ANALYSIS